IP Address
Word 3
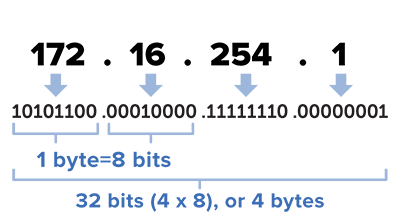
1. An Internet Protocol address (IP address) is a numerical label assigned to each device connected to a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. An IP address serves two principal functions: host or network interface identification and location addressing.
2. An IP address serves two principal functions. It identifies the host, or more specifically its network interface, and it provides the location of the host in the network, and thus the capability of establishing a path to that host. Its role has been characterized as follows: "A name indicates what we seek".
